
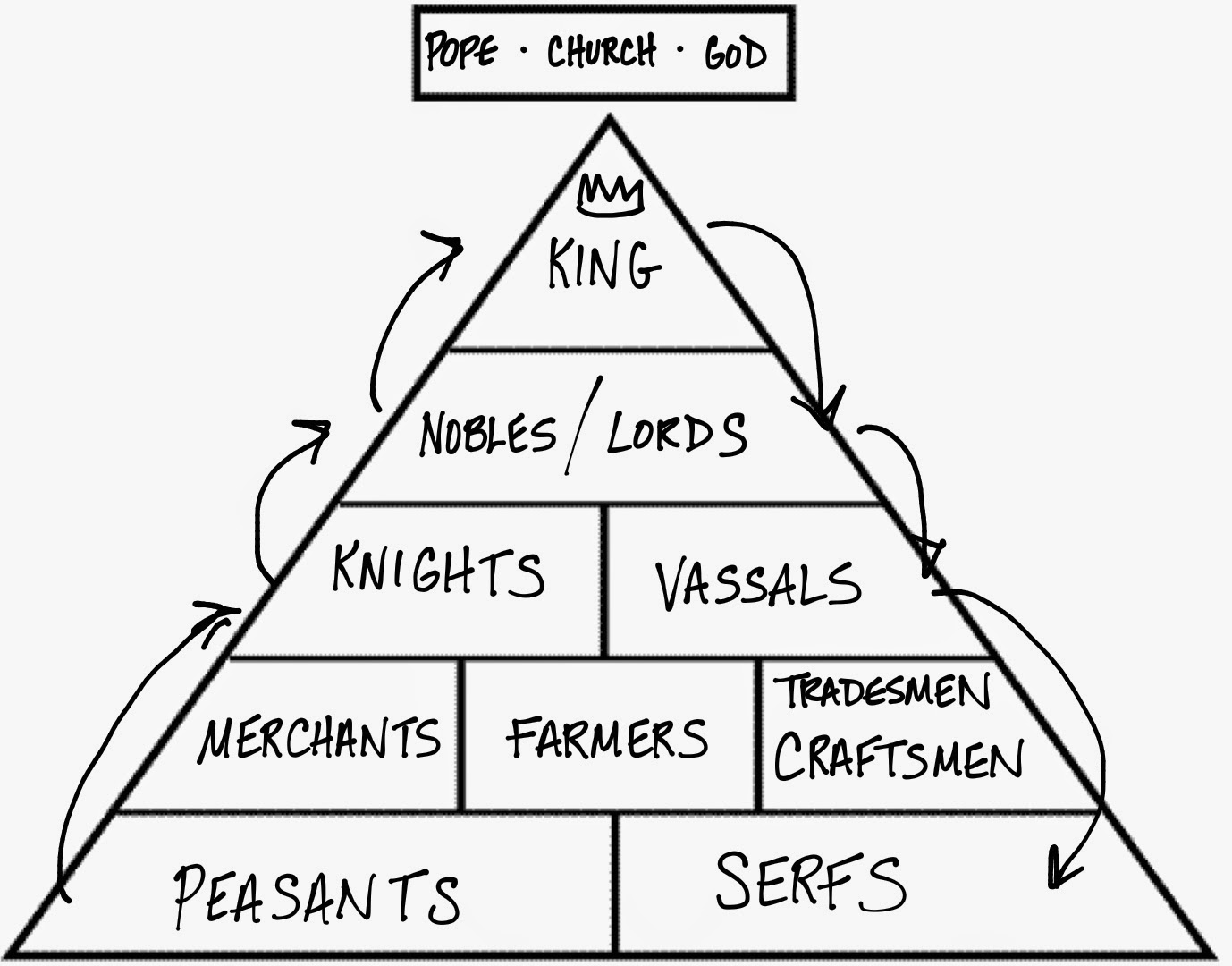
Another responsibility to the lord was to provide him with counsel whenever the lord needed advice or assistance from the vassals. It was expected that, having entered into agreement with the lord, the vassal would respond to a call of military duty whenever the lord thought it to be necessary. One, and the main, of the responsibilities was that he was expected to provide ‘aid’ or military service to the lord. The vassal was expected to perform some duties and responsibilities for as long as he was bound by the agreement. The public oath was referred to as “homage” (Bloch, 1961). This was to be done publicly in an oath of faithfulness (fealty). In the even of the vassal’s, the one in contract with the lord, death, it was his heir’s obligation to see to it that he has renewed the contract. A vassal held land, also known as fief, from the lord in exchange for his service in the army or in combat. It was basically a win-win situation for both parties. The relationship between the vassals and the lords was base on an understanding between the two parties. What was the relationship between the vassals and the lords? The system was built upon a relationship of obligation and mutual service between the vassals and the lords (Cantor, 1991).


The vassals, as mentioned in the introduction, were the persons who paid homage and pledged allegiance to the lords in exchange for the piece of land. It was the lords that administered justice, levied taxes and demanded military service from the vassals. They owned estates and large tracks of land. Power, in this case, was vested in the lords and barons. The social structure in the country in such a way that power was not vested on a single entity. The conclusion will then be given based on the comparison between the feudal system and the present system of authority. Factors that led to the collapse of the system will also be looked at briefly. The paper will seek to give a clear and concise outlook of the system by looking at the characteristics and the features of the system. The medieval period in Europe was characterized by hereditary systems of governance. This paper seeks to analyze and discuss this issue. It was just to make the lords feel as though they were not inferior to each other ( Bloch, 1961). The king’s position was basically a formality. The lords held the supreme authority over the area. Although there was the presence of the king, the position was irrelevant in the country. Vassals paid homage and allegiance to the lords and were from then on supposed to serve the lord and their country in as far as military aid was concerned. In this system, vassals gave military and other services to their lords in exchange for protection and the use of the land. Feudalism is defined as a social, economic and political system of Western Europe in the middle ages.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
